Definition
A world model is defined as an internal representation of the world that enables an artificial intelligence to understand its environment, make predictions about the future and make decisions based on these predictions (LeCun, 2022). These models combine elements of machine learning, neural networks and symbolic methods to develop a comprehensive understanding of complex dynamic systems and help AI agents to operate more effectively in the real world.
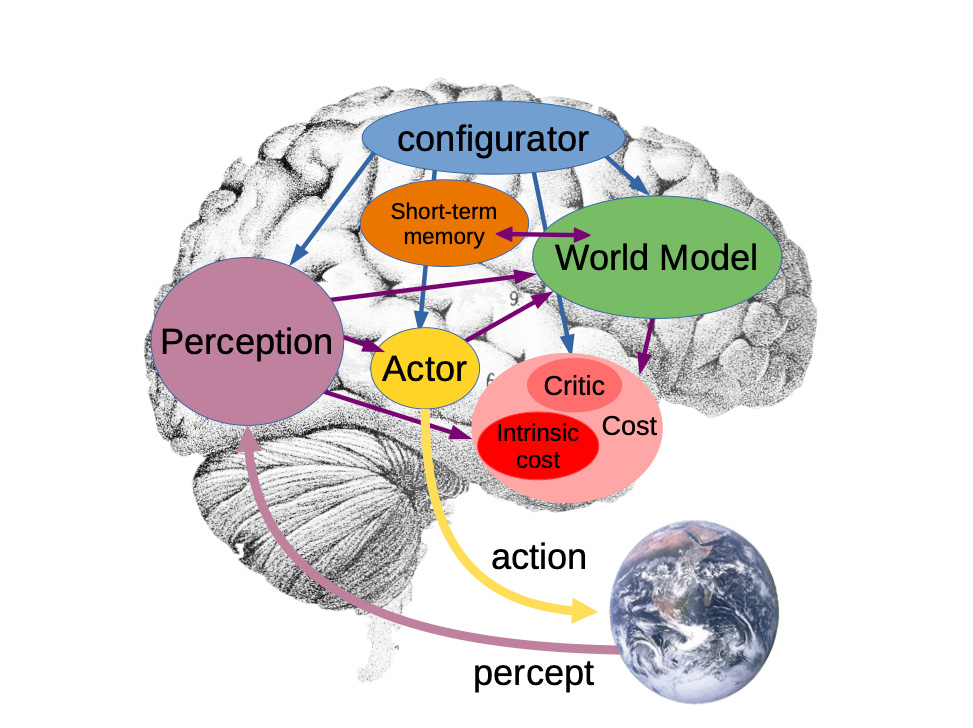
Functionality and architecture
World models use a hierarchical structure that encompasses different levels of abstraction and makes it possible to recognise both local and global relationships in data. The aim is to create a compact yet informative model that is capable of serving both planning and learning from experience (Ha & Schmidhuber, 2018).
Historical development
The idea of world models is not new, but has undergone a remarkable evolution since the early research on artificial intelligence. The realisation that agents do not just perform simple reactions but need an internal representation of their activities has been driven by work in robotics and cognitive science (Russell & Norvig, 2020).
Applications and challenges
World models are used in various fields, including autonomous driving, robotics and virtual reality. However, a key concern remains the challenge of developing a model that accurately and robustly represents reality. The difficulties lie in accurately representing uncertainties, temporal sequences and complex interactions within the environment (Battaglia et al., 2018).
Future prospects
Future research on world models aims to improve their ability to generalise and predict. Newer approaches, such as those based on neural differentiability and probabilistic programming, could lead to world models becoming more versatile and powerful (Bengio, 2013).
References
Battaglia, P. W., Hamrick, J. B., Pachter, L., & Tenenbaum, J. B. (2018). Communicating Autonomous Agents with Language. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(16), 4214-4219.
Bengio, Y. (2013). Deep Learning of Representations: Looking Forward. In D. A. Becker & A. M. Koller (Eds.), Representation Learning: From Awareness to Adaptation (pp. 507-516). Springer.
Ha, D., & Schmidhuber, J. (2018). World Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.10122.
LeCun, Y. (2022). A Path Towards Autonomous AI. Journal of AI Research, 1(1), 1-30.
Russell, S., & Norvig, P. (2020). Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (4th ed.). Pearson.